Ascites is the pathologic accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Paracolic gutter ascites.
Unlike fluid seen in vessels or the bladder that have contained borders ascites fills potential spaces in the abdomen and pelvis.
Various tumours and tumour like conditions can mimic p.
Based on how fluid travels in the abdomen the most likely place to find fluid is in the right upper quadrant and pelvis.
Hemoperitoneum starts near the site of injury and flows along expected anatomic pathways.
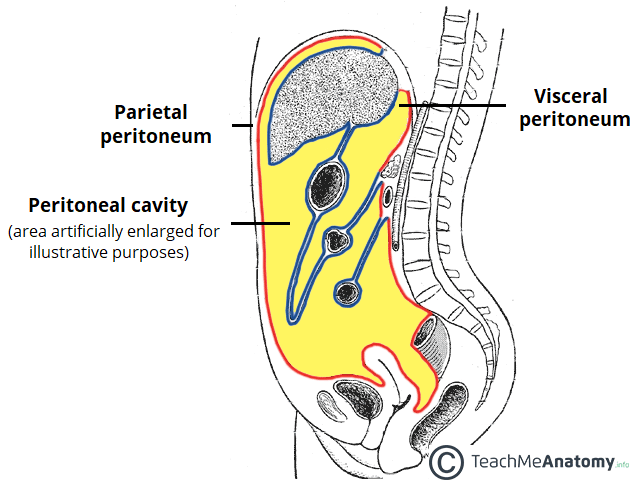
Hemorrhage from the liver typically flows in a caudal direction from the perihepatic spaces and hepatorenal fossa along the right paracolic gutter and into the cul de sac which is the rectouterine space in women and rectovesical space in men fig 1.
Typical transudative ascites has density of 0 15 hounsfield units hu and appears free flowing.
The imaging findings vary from simple ascites to multifocal discrete nodules and infiltrative peritoneal masses.
The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and communicates freely with the right subphrenic space.
Computed tomography is particularly important for detailed preoperative assessment and evaluation of the radiological peritoneal cancer index.
Visualized pancreas shows dilated main pancreatic duct 4 5 mm.
Both paracolic gutters run laterally along the back side of the abdominal wall and are situated between the abdominal wall and the outer margin of the colon.
The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon.
Tiny echoes are present in ascites compare with urinary bladder without echoes.
The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side.
The paracolic spaces gutters are located lateral to the peritoneal reflections of the left and right sides of the colon fig 8a.
Paracolic gutters help keep infectious material away from the body s internal organs.
Larger amounts of fluid accumulate in paracolic gutters.
Traditionally paracentesis was performed blindly using standard anatomical landmarks.
Ultrasound gross amount of free fluid is noted in hepatorenal splenorenal perihepatic perisplenic both paracolic gutters both iliac fossa and pelvic.
Small amounts of ascites typically seen in right perihepatic space morison pouch and pouch of douglas.
In some disorders peritoneal fluid represents a complication or late manifestation of disease whereas in others it is the first clinical expression of the disease process.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon possesses a short mesentery for part of its length.
Ascites can cause centralization of bowel loops.
As the etiology of ascites in most patients is liver cirrhosis with associated portal hypertension the liver typically becomes smaller and the spleen larger as disease progresses.
Pc is most commonly seen in abdominopelvic malignancies.
The right lateral gutter is much larger and allows for greater drainage than the left gutter.